
WHAT IS GST?
GST i.e.Goods and Service Tax is a unified tax that replaces several indirect taxesleviedby the Central Government and the State Government(s)....
Read more|
Circular No. 181/7/2014-Service Tax F. No. 137/46/2014-Service Tax Government of India Ministry of Finance Department of Revenue Central Board of Excise and Customs
New Delhi, the 10th December, 2014
To,
All Principal Chief Commissioners / Chief Commissioners of Central Excise/Service Tax Principal Directors General/ Director General Service Tax/ DGCEI/Systems/ Audit All Principal Commissioners/Commissioners of Central Excise/Service Tax All Principal Additional Directors General/ Additional Directors General Audit
Madam/Sir
Sub: Audit of the Service Tax assessees by the officers of Service Tax and Central Excise Commissionerates
Section 94 of the Finance Act, 1994 deals with rule making powers of the Central Government in relation to service tax. Sub-section (2) of section 94, dealing with specific purposes for which rules can be made, was amended with effect from 06.08.2014, vide Section 114(J) of the Finance Act, 2014, and a new clause (k) was added to sub-section (2) of section 94, which is reproduced below –
“(k) imposition, on persons liable to pay service tax, for the proper levy and collection of tax, of duty of furnishing information, keeping records and the manner in which such records shall be verified.”
2. In exercise of the rule making powers under clause (k) of sub-section (2) of section 94 of the Finance Act, 1994, the Central Government has inserted a new rule 5(A)(2) in the Service Tax Rules, 1994 vide notification no. 23/2014-Service Tax dated 5th December, 2014. This rule, interalia, provides for scrutiny of records by the audit party deputed by the Commissioner. Such scrutiny essentially constitutes audit by the audit party consisting of departmental officers.
3. Verification of records mandated by the statute is necessary to check the correctness of assessment and payment of tax by the assessee in the present era of self-assessment. It may be noted that the expression “verified” used in section 94(2)(k) of the said Act is of wide import and would include within its scope, audit by the departmental officers, as the procedure prescribed for audit is essentially a procedure for verification mandated in the statute.
4. It may also be noted that the Hon’ble High Court of Delhi in the judgment dated 04.08.2014 in the case of M/s Travelite (India) [2014-TIOL-1304-HC-DEL-ST] had quashed rule 5A(2) of the Service Tax Rules, 1994 on the ground that the powers to conduct audit envisaged in the rule did not have appropriate statutory backing. This judgment can now be distinguished as a clear statutory backing for the rule now exists in section 94(2)(k) of the said Act.
5. Departmental officers are directed to audit the Service Tax assessees as provided in the departmental instructions in this regard. Difficulty, if any, in implementing the circular may be brought to the notice of the Board. Hindi version will follow.
(Himani Bhayana) Under Secretary (Service Tax)
|

GST i.e.Goods and Service Tax is a unified tax that replaces several indirect taxesleviedby the Central Government and the State Government(s)....
Read more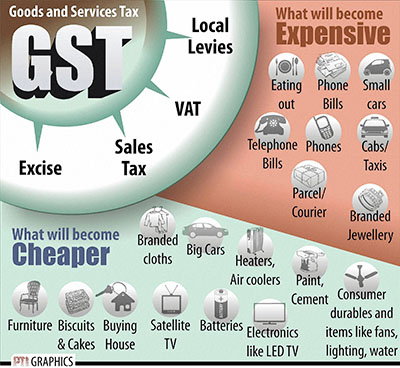
In pre-GST regime, goodswere liable to: (i) Excise Duty- on manufacture of goods; (ii) VAT/CST- on sale of goods; (iii) Entry tax- on ...
Read more
GST is levied on every taxable person. Taxable person means a person who carries on any business at any place in India. Such . ..
Read more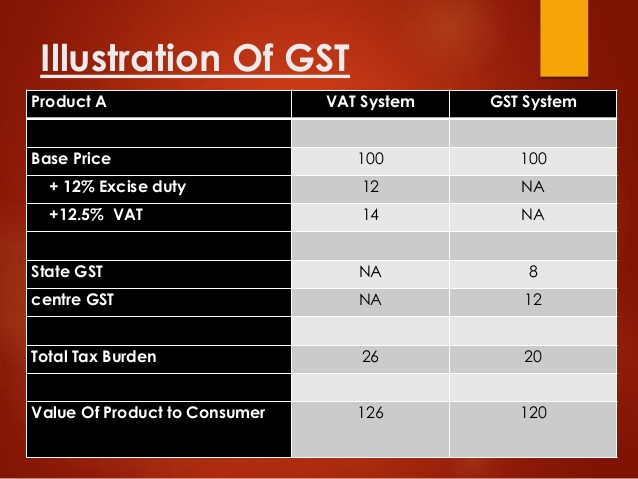
GST is a unified tax which is levied on: (i) goods; (ii) services and (iii) a mix of goods and/or services. Any supply of goods or services . .. ...
Read moreGST India Solution is an effort of firm of professionals who welcome implementation of GST. This is an interactiveplatformthat aspires to disseminate right knowledge to professionals, practitioners and public at large. This platform has beenfloatedbya firm of Chartered Accountants relentlessly working in field of direct and indirect taxes since early 1985.
READ MORE
Our core competence is statutory compliance, advisory, corporate tax planning and appellate matters of direct and indirect taxesandcorporate training sessions on GST.
The senior partner of the firm has to his credit several professional publications viz., Delhi Sales Tax Right to Use Goods Act, Delhi VAT, Maharashtra VAT, West Bengal VAT, Haryana VAT published by Taxmann. Madhya Pradesh VAT and Chhattisgarh VAT were published by Suvidha Law House, Bhopal. He has also addressed seminars on indirect taxes organized by professional bodies like ICAI, IMA, NIFM etc. and has also contributed articles on subjects of pro. . . . .