
WHAT IS GST?
GST i.e.Goods and Service Tax is a unified tax that replaces several indirect taxesleviedby the Central Government and the State Government(s)....
Read more| 41. Procedures for sale of property held by the Commissioner . | |
|
41. Procedures for sale of property held by the Commissioner .
(1) Where the Commissioner has in his possession any goods, goods vehicle, or any other property, including goods seized at any border or check-post and goods held as security for the performance of an obligation under the Act (in this rule called “the property”), which may be sold by the Commissioner in pursuance of any powers conferred under the Act to recover tax, interest, penalty or other amount due under the Act, the power of sale shall be exercised in the manner set out in this rule.
(2) The Commissioner shall serve a notice in Form DVAT-29 in the manner prescribed in rule 62 on the person recorded as the owner of the goods in the Commissioner’s records requiring the person to redeem the property within fifteen
days by tender of payment in cash of all amounts owed under the Act.
(3) Where the person has not redeemed the property within the time specified in the form, the Commissioner may proceed to sell the property by public auction as per the following procedure
(a) A report shall be prepared of the facts and circumstances in which the property is required to be sold by public auction and the Commissioner shall make a written order for sale or disposal of the property.
(b) The officer nominated by the Commissioner for the purpose shall cause to be published on the notice board of his office, a list of the properties intended for sale with a notice under his signature specifying the place where, and the day and hour at which, the property is to be sold and display copies of such list and notices at more than one public place near the place where the property is currently held, and the place of the proposed auction. A copy of the list and notice shall also be displayed in the office of the Commissioner. Except in exceptional circumstances, a notice for not less than seven days shall be given before the auction is conducted.
(c) Intending bidders shall be required to deposit as earnest money, a sum equal to ten per cent of the estimated value of the property. The officer conducting the auction shall prepare a receipt acknowledging the receipt of the earnest money.
Earnest money deposited by unsuccessful bidders shall be refunded to them immediately after the auction is over.
(d) At the appointed day and time, the property shall be put up in one or more lots, as the officer conducting the auction sale may consider fit and shall be knocked down in favour of the highest bidder subject to confirmation of the sale by the Commissioner.
(e) The purchaser shall pay the sale value of the property in cash immediately after the sale and he shall not be permitted to carry away any part of the property until he has paid for the same in full and until the sale has been confirmed by the Commissioner. If the purchaser fails to pay the purchase money within three days of the confirmation of sale by the Commissioner, the property shall be re-offered for
auction and any earnest money deposited by the defaulting bidder shall be forfeited to the Government.
(4) If any order directing detention is reversed on appeal, the property detained, to the extent they have not been sold before such reversal comes to the knowledge of the officer conducting the sale, shall be released or, if such property has been sold, the net proceeds thereof shall be paid to the owner of the property.
(5) Notwithstanding anything contained in this rule, if the property is of a perishable nature or subject to speedy and natural decay or when the expenses of keeping it in custody are likely to be high, the Commissioner may –
(a) reduce the time stated in sub-rule (2) within which the owner may redeem the property;
(b) reduce the time for display of any notice; and
(c) accelerate the time for conducting the auction of the property.
(6) Where property is sold under the preceding sub-rules, the proceeds of sale shall be applied in the following order –
(a) payment of any expenses of the sale, including tax arising under the Act by virtue of the sale, and other incidental charges;
(b) in respect of any surplus, payment of the amount of any tax, interest and penalty recoverable under the Act or Delhi Sales Tax Act, 1975 (43 of 1975) or the Delhi Sales Tax on Works Contract Act, 1999 (Delhi Act 9 of 1999) or the Central Sales Tax Act, 1956 (74 of 1956) or The Delhi Sales Tax on Right to Use Goods Act, 2002 (Delhi Act 13 of 2002);
(c) in respect of any surplus, on application made to the Commissioner and upon provision of sufficient proof, payment to the person who was the owner of the property; and
(d) in respect of any surplus, in the absence of any claimant, deposited in the Consolidated Fund of the National Capital Territory of Delhi.
|
|

GST i.e.Goods and Service Tax is a unified tax that replaces several indirect taxesleviedby the Central Government and the State Government(s)....
Read more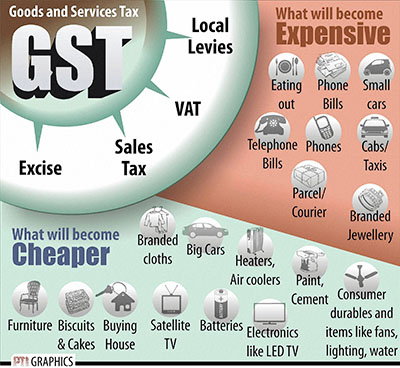
In pre-GST regime, goodswere liable to: (i) Excise Duty- on manufacture of goods; (ii) VAT/CST- on sale of goods; (iii) Entry tax- on ...
Read more
GST is levied on every taxable person. Taxable person means a person who carries on any business at any place in India. Such . ..
Read more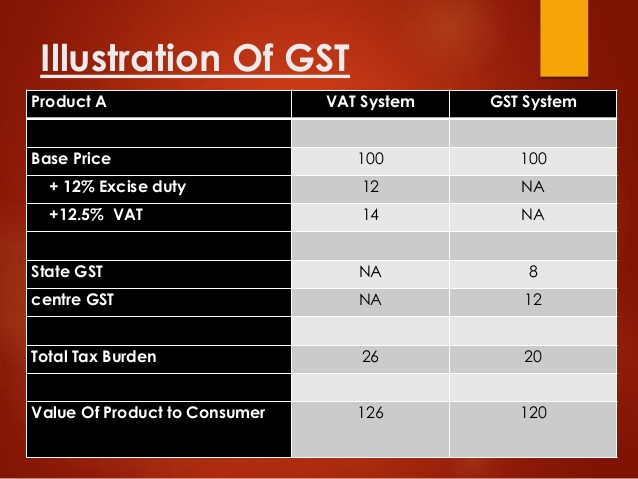
GST is a unified tax which is levied on: (i) goods; (ii) services and (iii) a mix of goods and/or services. Any supply of goods or services . .. ...
Read moreGST India Solution is an effort of firm of professionals who welcome implementation of GST. This is an interactiveplatformthat aspires to disseminate right knowledge to professionals, practitioners and public at large. This platform has beenfloatedbya firm of Chartered Accountants relentlessly working in field of direct and indirect taxes since early 1985.
READ MORE
Our core competence is statutory compliance, advisory, corporate tax planning and appellate matters of direct and indirect taxesandcorporate training sessions on GST.
The senior partner of the firm has to his credit several professional publications viz., Delhi Sales Tax Right to Use Goods Act, Delhi VAT, Maharashtra VAT, West Bengal VAT, Haryana VAT published by Taxmann. Madhya Pradesh VAT and Chhattisgarh VAT were published by Suvidha Law House, Bhopal. He has also addressed seminars on indirect taxes organized by professional bodies like ICAI, IMA, NIFM etc. and has also contributed articles on subjects of pro. . . . .