
WHAT IS GST?
GST i.e.Goods and Service Tax is a unified tax that replaces several indirect taxesleviedby the Central Government and the State Government(s)....
Read more| 86 Penalties | |
|
CHAPTER XIII
Penalties and Offences
86 Penalties
[(1) In this section “tax deficiency” means the difference between the tax properly payable by the person in accordance with the provisions of this Act and the amount of tax paid by the person in respect of a calendar month.
Explanations-1 - ‘Tax properly payable’ includes the amount of tax assessed under section 32 of the ‘Act’.
2. Due tax paid after the period specified in sub-section (4) of section
3 of the Act, is also a tax deficiency.]
(2) The Government may, from time to time, if it deems it necessary, vary the amount of any penalty due under this section by a notification to that effect in the official Gazette:
PROVIDED that any penalty which is increased under this section shall have effect only for offences or failures occurring after the date of such notification;
“PROVIDED FURTHER that the penalty imposed under this section can be remitted where a person is able to prove existence of a reasonable cause for the act or omission giving rise to penalty during objection proceedings under section 74 of this Act
(3) Where two or more penalties arise under this Act in respect of the same conduct of a person, the person shall be liable to pay only the greater penalty.
[(4) Where a person who is required to be registered under this Act has failed to apply for registration within one month from the day on which the requirement arose, the person shall be liable to pay, by way of penalty, an amount equal to one thousand rupees per day from the day immediately following the expiry of the said period until the person makes an application for registration in the prescribed form, containing such particulars and information and accompanied by such fee, security and other documents as may be prescribed:
PROVIDED that the amount of penalty payable under this sub-section shall not exceed one lakh rupees.]
(5) If, a registered dealer fails to comply with the provisions of sub-section (1) of section 21 of this Act, the person shall be liable to pay, by way of penalty, a sum of 1[five] hundred rupees per day of default subject to a maximum of 2[ten] thousand rupees.
(6) If a registered dealer –
(a) fails to comply with the provisions of sub-section (2) of section 22 of this Act; or
(b) fails to surrender his certificate of registration as provided in sub-section (7) of section 22 of this Act;
the registered dealer shall be liable to pay, by way of penalty, a sum equal to one 3[thousand] rupees for every day of default subject to a maximum of 4[twenty five] thousand rupees.
(7) If any person falsely represents that he is registered as a dealer under this Act, he shall be liable to a penalty equal to the amount of tax wrongly collected or one lakh rupees, whichever is the greater.
(8) Where a person –
(a) has applied for registration under sub-section (4) of section 18 of this Act;
(b) has been registered; and either –
(i) has failed to undertake activities which would make the person a dealer within the period specified in his application; or
(ii) has failed to comply with any of the restrictions or conditions subject to which such registration was granted, the person shall be liable to pay a penalty of ten thousand rupees.
[(9) If a person required to furnish a return under Chapter V or to comply with a requirement in a notification issued under section 70 of this Act -
(a) fails to furnish any return by the due date; or
(b) fails to furnish with a return any other document that is required to be furnished with the return; or
(c) being required to revise a return already furnished, fails to furnish the revised return by the due date; or
(d) fails to comply with a requirement in a notification issued under section 70; the person shall be liable to pay, by way of penalty, a sum of five hundred rupees per day from the day immediately following the due date until the failure is rectified:
PROVIDED that the amount of penalty payable under this sub-section shall not exceed fifty thousand rupees.]
(10) Any person who –
(a) furnishes a return under this Act which is false, misleading or deceptive in a material particular; or
(b) omits from a return furnished under this Act any matter or thing without which the return is false, misleading or deceptive in a material particular; shall be liable to pay, by way of penalty, a sum of ten thousand rupees or theamount of the tax deficiency, whichever is the greater.
(11) Any dealer who –
(a) has claimed tax credit under section 14 of this Act to which he is not entitled; or
(b) has claimed a greater tax credit under section 14 than is allowed; shall be liable to pay, by way of penalty, an amount equal to the amount of tax credit so claimed or ten thousand rupees, whichever is the greater.
(12) Where a tax deficiency arises in relation to a person, the person shall be liable to pay, by way of penalty, a sum equal to one per cent of the tax deficiency per week or a sum equal to rupees one hundred per week, whichever is higher, for the period of default.
(13) Where a person is required under this Act to –
(a) prepare records or accounts; or
(b) prepare records or accounts in a prescribed manner; or
[(c) retain prescribed or notified records or accounts; and the person -
(i) fails to prepare the prescribed or notified records and accounts; or
(ii) fails to prepare prescribed or notified records and accounts in the prescribed manner; or
(iii) fails to retain the prescribed or notified records and accounts for the prescribed period; or
(iv) fails to retain and/or produce the prescribed or notified records at theprincipal place of business as recorded in his certificate of registration; or
(v) fails to comply with a direction issued or fails to produce prescribed or notified records and accounts, or cause them to be produced, on or before the date specified in any notice served on him by the Commissioner or by an accountant or a panel of accountants or any other professional or panel of professionals nominated by the Commissioner in this behalf under sub-section (1) of section 58A; the person shall be liable to pay, by way of penalty, a sum of fifty thousand rupees or twenty per cent of the tax deficiency, if any, whichever is greater.]
(14) Any person who fails to comply with the requirement under sub-section (2) or sub-section (3) of section 59 of this Act shall be liable to pay, by way of penalty, a sum of fifty thousand rupees.
(15) Where a person who is required to prepare records and accounts under this Act, prepares records and accounts in a manner that is false, misleading or deceptive, the person shall be liable to pay, by way of penalty, a sum of one lakh rupees or the amount of the tax deficiency, if any, whichever is greater.
(16) Where a person –
(a) has issued a tax invoice or retail invoice with incomplete or incorrect particulars; or
(b) having issued a tax invoice or retail invoice, has failed to account it correctly in his books of account; the person shall be liable to pay, by way of penalty, an amount of five thousand rupees or twenty per cent of the tax deficiency, if any, whichever is greater.
(17) Where a person who is not authorised under this Act to issue a tax invoice has issued a tax invoice for a sale, the person shall be liable to pay, by way of penalty, an amount of one lakh rupees or the tax deficiency, if any, whichever is greater.
[(18) If, any dealer fails to comply with the provisions of section 49 of this Act, the dealer shall be liable to pay, by way of penalty, a sum equal to one percent of his turnover or a sum of one lakh rupees, whichever is less.]
(19) Where goods are being carried by a transporter without the documents or without proper and genuine documents or without being properly accounted for in the documents referred to in sub-section (2) of section 61 of this Act, the transporter shall be liable to a penalty equal to 2[twenty] paisa in a rupee for the value of such goods].
(20) Any person who –
(a) makes a statement to the Commissioner which is false, misleading or deceptive in a material particular; or
(b) omits from a statement made to the Commissioner any matter or thing without which the statement is false, misleading or deceptive in a material particular; the person shall be liable to pay, by way of penalty, a sum of fifty thousand rupees, or the amount of the tax deficiency, whichever is greater.
Explanation.- The liability to pay a penalty and the amount of the penalty may be the subject of an objection under section 74 of this Act.
1[(21) Where a casual trader who is required to be registered under this Act has failed to apply for registration within stipulated period, the casual trader shall be liable to pay, by way of penalty, an amount equal to five thousand rupees per day, from the day immediately following the expiry of the due date until the person makes an application for registration under this Act :
PROVIDED that the amount of penalty payable under this sub-section shall not exceed one lakh rupees.
(22) If a casual trader required to furnish a return under this Act–
(a) fails to furnish any return by the due date; or
(b) fails to furnish with a return any other document that is required to be furnished with the return;
the person shall be liable to pay, by way of penalty, a sum of one thousand rupees per day from the day immediately following the due date until the failure is rectified:
PROVIDED that the amount of penalty payable under this sub-section shall not exceed 2[twenty five] thousand rupees.
(23) Where any person who, whether as principal, agent or in any other capacity
organizes any exhibition-cum-sale in Delhi and fails –
(a) to furnish any information in respect of the goods brought or kept in stock or sold by any participant before or during or after the exhibition-cum-sale; or
(b) to ensure that all such participants in the exhibition-cum-sale have obtained registration under this Act and paid due tax; or
(c) to permit inspection of the business premises or goods or account and records of the participants; or
(d) to permit inspection of the accounts and records of the organizer in respect of the exhibition-cum-sale; such person shall be liable to pay, by way of penalty, a sum equal to fifty thousand rupees or a sum equal to the amount of tax payable on such goods if such goods were sold in Delhi, whichever is greater.]
[(24) Any person, who contravenes any of the provisions of this Act or any rules made thereunder for which no penalty is separately provided under the Act,shall be liable to pay a penalty of ten thousand rupees.]
|
|

GST i.e.Goods and Service Tax is a unified tax that replaces several indirect taxesleviedby the Central Government and the State Government(s)....
Read more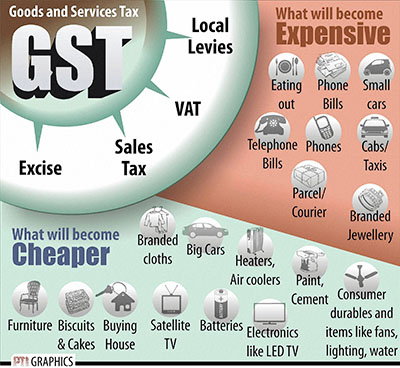
In pre-GST regime, goodswere liable to: (i) Excise Duty- on manufacture of goods; (ii) VAT/CST- on sale of goods; (iii) Entry tax- on ...
Read more
GST is levied on every taxable person. Taxable person means a person who carries on any business at any place in India. Such . ..
Read more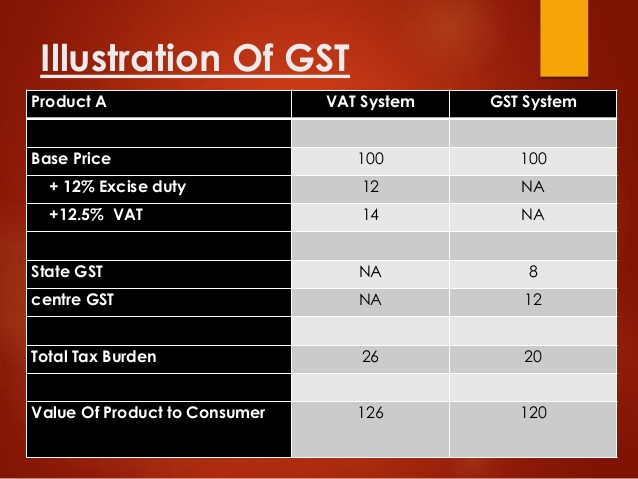
GST is a unified tax which is levied on: (i) goods; (ii) services and (iii) a mix of goods and/or services. Any supply of goods or services . .. ...
Read moreGST India Solution is an effort of firm of professionals who welcome implementation of GST. This is an interactiveplatformthat aspires to disseminate right knowledge to professionals, practitioners and public at large. This platform has beenfloatedbya firm of Chartered Accountants relentlessly working in field of direct and indirect taxes since early 1985.
READ MORE
Our core competence is statutory compliance, advisory, corporate tax planning and appellate matters of direct and indirect taxesandcorporate training sessions on GST.
The senior partner of the firm has to his credit several professional publications viz., Delhi Sales Tax Right to Use Goods Act, Delhi VAT, Maharashtra VAT, West Bengal VAT, Haryana VAT published by Taxmann. Madhya Pradesh VAT and Chhattisgarh VAT were published by Suvidha Law House, Bhopal. He has also addressed seminars on indirect taxes organized by professional bodies like ICAI, IMA, NIFM etc. and has also contributed articles on subjects of pro. . . . .