
WHAT IS GST?
GST i.e.Goods and Service Tax is a unified tax that replaces several indirect taxesleviedby the Central Government and the State Government(s)....
Read more| 76 Appeals to Appellate Tribunal | |
|
76 Appeals to Appellate Tribunal
[(1) Any person aggrieved by a decision made by the Commissioner under sections 74, 84 and 85 of this Act may appeal to the Appellate Tribunal against suchdecision:
PROVIDED that no appeal may be made against a non-appealable order under section 79 of this Act.
Explanation.– The Commissioner does not appeal to the Appellate Tribunal but may make a re-assessment of tax where he is of the opinion that further tax is owed.]
(2) Subject to the provisions of section 77 of this Act, no appeal shall be entertained unless it is made within two months from the date of service of the decision appealed against.
(3) Every appeal made under this section shall be in the prescribed form,verified in the prescribed manner and shall be accompanied by such fee as may beprescribed.
(4) No appeal against an assessment shall be entertained by the Appellate Tribunal unless the appeal is accompanied by satisfactory proof of the payment of the amount in dispute and any other amount assessed as due from the person:
PROVIDED that the Appellate Tribunal may, if it thinks fit, for reasons to be recorded in writing, entertain an appeal against such order without payment of some or all of the amount in dispute, on the appellant furnishing in the prescribed manner security for such amount as it may direct:
PROVIDED FURTHER that no appeal shall be entertained by the Appellate Tribunal unless it is satisfied that such amount as the appellant admits to be due from him has been paid.
(5) In proceedings before the Appellate Tribunal –
(a) the person aggrieved shall be limited to disputing only those matters stated in the objection;
(b) the person aggrieved shall be limited to arguing only those grounds stated in the objection; and
(c) the person aggrieved may be permitted to adduce evidence not presented to the Commissioner for good and sufficient reasons.
“(1) Any person aggrieved by a decision made by the Commissioner under section 74 of this Act may appeal to the Appellate Tribunal against such decision:
PROVIDED that no appeal may be made against a non-appealable order under section 79 of this Act.
Explanation.- The Commissioner does not appeal to the Appellate Tribunal. The Commissioner may make a further assessment of tax where he is of the opinion that further tax is owed.”.
(6) The Appellate Tribunal shall –
(a) in the case of an assessment, confirm, reduce, or annul the assessment (including any penalty and interest imposed);
(b) in the case of any other decision of the Commissioner, affirm or reject the decision; or
(c) pass such other order for the determination of the issue as it thinks fit:
PROVIDED that the Appellate Tribunal shall give reasons in writing for its decision which shall include its findings on material questions of fact and the evidence or other material on which those findings were based.
(7) The Appellate Tribunal shall use its best endeavours to make a final resolution of the matter before it and for this purpose may make a decision in substitution for the order in dispute, including the exercise or re-exercise of any discretion or power vested in the Commissioner.
(8) The Appellate Tribunal shall not set aside an assessment and remit the matter to the Commissioner for a further assessment, unless it has first –
(a) advised the aggrieved person of the proposed order;
(b) offered the person the opportunity to adduce such further evidence before it as might assist the Appellate Tribunal to reach a final determination.
(9) Where the Appellate Tribunal sets aside an assessment and remits the matter
to the Commissioner for a further assessment, the Appellate Tribunal shall at the same time order the Commissioner to refund to the person some or all of the amount in dispute:
PROVIDED that where no order is made, it shall be presumed that the Appellate Tribunal has ordered the refund of the amount in dispute.
(10) Where a person has failed to attend the hearing at the time and place stipulated, the Appellate Tribunal may adjourn the proceedings, strike out the appeal or proceed to make an order determining the objection in the absence of the person.
(11) Save as provided in section 81 and sub-section (12) of this section, an order passed by the Appellate Tribunal on an appeal shall be final.
(12) The Appellate Tribunal may rectify any mistake or error apparent from the record of its proceedings.
[(13) Any order passed by the Appellate Tribunal may be reviewed suo-motu or upon an application made in that behalf:
PROVIDED that before any order which is likely to affect any person adversely is passed, such person shall be given a reasonable opportunity of being heard.]
|
|

GST i.e.Goods and Service Tax is a unified tax that replaces several indirect taxesleviedby the Central Government and the State Government(s)....
Read more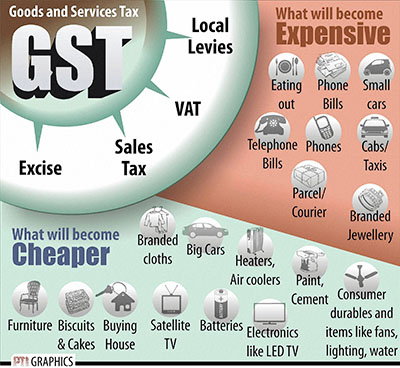
In pre-GST regime, goodswere liable to: (i) Excise Duty- on manufacture of goods; (ii) VAT/CST- on sale of goods; (iii) Entry tax- on ...
Read more
GST is levied on every taxable person. Taxable person means a person who carries on any business at any place in India. Such . ..
Read more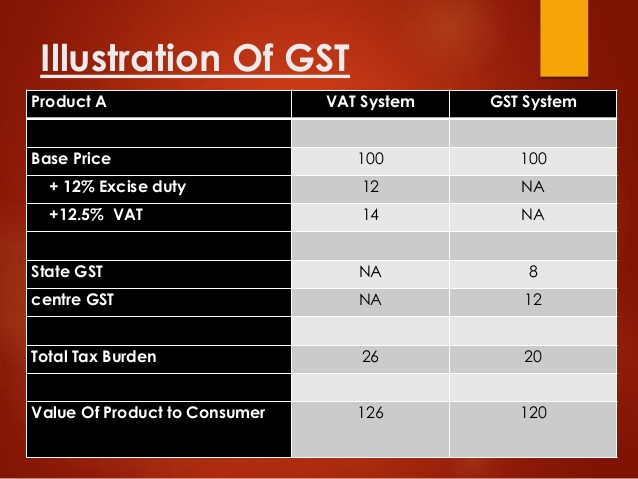
GST is a unified tax which is levied on: (i) goods; (ii) services and (iii) a mix of goods and/or services. Any supply of goods or services . .. ...
Read moreGST India Solution is an effort of firm of professionals who welcome implementation of GST. This is an interactiveplatformthat aspires to disseminate right knowledge to professionals, practitioners and public at large. This platform has beenfloatedbya firm of Chartered Accountants relentlessly working in field of direct and indirect taxes since early 1985.
READ MORE
Our core competence is statutory compliance, advisory, corporate tax planning and appellate matters of direct and indirect taxesandcorporate training sessions on GST.
The senior partner of the firm has to his credit several professional publications viz., Delhi Sales Tax Right to Use Goods Act, Delhi VAT, Maharashtra VAT, West Bengal VAT, Haryana VAT published by Taxmann. Madhya Pradesh VAT and Chhattisgarh VAT were published by Suvidha Law House, Bhopal. He has also addressed seminars on indirect taxes organized by professional bodies like ICAI, IMA, NIFM etc. and has also contributed articles on subjects of pro. . . . .