
WHAT IS GST?
GST i.e.Goods and Service Tax is a unified tax that replaces several indirect taxesleviedby the Central Government and the State Government(s)....
Read more|
Removal, resignation of auditor and giving of special notice (1) The auditor appointed under section 139 may be removed from his office before the expiry of his term only by a special resolution of the company, after obtaining the previous approval of the Central Government in that behalf in the prescribed manner: Provided that before taking any action under this sub-section, the auditor concerned shall be given a reasonable opportunity of being heard. (2) The auditor who has resigned from the company shall file within a period of thirty days from the date of resignation, a statement in the prescribed form with the company and the Registrar, and in case of companies referred to in sub-section (5) of section 139, the auditor shall also file such statement with the Comptroller and Auditor-General of India, indicating the reasons and other facts as may be relevant with regard to his resignation. [(3) If the auditor does not comply with the provisions of sub-section (2), he or it shall be liable to a penalty of fifty thousand rupees or an amount equal to the remuneration of the auditor, whichever is less, and in case of continuing failure, with a further penalty of five hundred rupees for each day after the first during which such failure continues, subject to a maximum of [two lakh rupees].] (4) (i) Special notice shall be required for a resolution at an annual general meeting appointing as auditor a person other than a retiring auditor, or providing expressly that a retiring auditor shall not be re-appointed, except where the retiring auditor has completed a consecutive tenure of five years or, as the case may be, ten years, as provided under sub-section (2) of section 139. (ii) On receipt of notice of such a resolution, the company shall forthwith send a copy thereof to the retiring auditor. (iii) Where notice is given of such a resolution and the retiring auditor makes with respect thereto representation in writing to the company (not exceeding a reasonable length) and requests its notification to members of the company, the company shall, unless the representation is received by it too late for it to do so,—
and if a copy of the representation is not sent as aforesaid because it was received too late or because of the company's default, the auditor may (without prejudice to his right to be heard orally) require that the representation shall be read out at the meeting: Provided that if a copy of representation is not sent as aforesaid, a copy thereof shall be filed with the Registrar: Provided further that if the Tribunal is satisfied on an application either of the company or of any other aggrieved person that the rights conferred by this sub-section are being abused by the auditor, then, the copy of the representation may not be sent and the representation need not be read out at the meeting. (5) Without prejudice to any action under the provisions of this Act or any other law for the time being in force, the Tribunal either suo motu or on an application made to it by the Central Government or by any person concerned, if it is satisfied that the auditor of a company has, whether directly or indirectly, acted in a fraudulent manner or abetted or colluded in any fraud by, or in relation to, the company or its directors or officers, it may, by order, direct the company to change its auditors: Provided that if the application is made by the Central Government and the Tribunal is satisfied that any change of the auditor is required, it shall within fifteen days of receipt of such application, make an order that he shall not function as an auditor and the Central Government may appoint another auditor in his place: Provided further that an auditor, whether individual or firm, against whom final order has been passed by the Tribunal under this section shall not be eligible to be appointed as an auditor of any company for a period of five years from the date of passing of the order and the auditor shall also be liable for action under section 447. Explanation I.—It is hereby clarified that the case of a firm, the liability shall be of the firm and that of every partner or partners who acted in a fraudulent manner or abetted or colluded in any fraud by, or in relation to, the company or its directors or officers.
Explanation II.—For the purposes of this Chapter the word "auditor" includes a firm of auditors. |

GST i.e.Goods and Service Tax is a unified tax that replaces several indirect taxesleviedby the Central Government and the State Government(s)....
Read more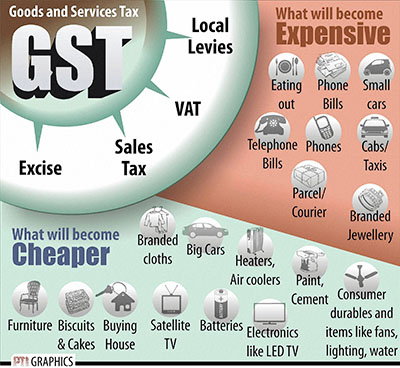
In pre-GST regime, goodswere liable to: (i) Excise Duty- on manufacture of goods; (ii) VAT/CST- on sale of goods; (iii) Entry tax- on ...
Read more
GST is levied on every taxable person. Taxable person means a person who carries on any business at any place in India. Such . ..
Read more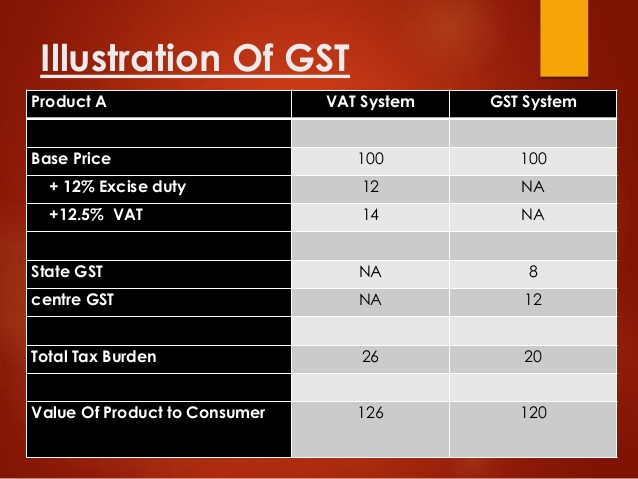
GST is a unified tax which is levied on: (i) goods; (ii) services and (iii) a mix of goods and/or services. Any supply of goods or services . .. ...
Read moreGST India Solution is an effort of firm of professionals who welcome implementation of GST. This is an interactiveplatformthat aspires to disseminate right knowledge to professionals, practitioners and public at large. This platform has beenfloatedbya firm of Chartered Accountants relentlessly working in field of direct and indirect taxes since early 1985.
READ MORE
Our core competence is statutory compliance, advisory, corporate tax planning and appellate matters of direct and indirect taxesandcorporate training sessions on GST.
The senior partner of the firm has to his credit several professional publications viz., Delhi Sales Tax Right to Use Goods Act, Delhi VAT, Maharashtra VAT, West Bengal VAT, Haryana VAT published by Taxmann. Madhya Pradesh VAT and Chhattisgarh VAT were published by Suvidha Law House, Bhopal. He has also addressed seminars on indirect taxes organized by professional bodies like ICAI, IMA, NIFM etc. and has also contributed articles on subjects of pro. . . . .