
WHAT IS GST?
GST i.e.Goods and Service Tax is a unified tax that replaces several indirect taxesleviedby the Central Government and the State Government(s)....
Read more|
115JG.Conversion of an Indian branch of foreign company into subsidiary Indian company. —(1) Where a foreign company is engaged in the business of banking in India through its branch situate in India and such branch is converted into a subsidiary company thereof, being an Indian company (hereafter referred to as an Indian subsidiary company) in accordance with the scheme framed by the Reserve Bank of India, then, notwithstanding anything contained in the Act and subject to the conditions as may be notified by the Central Government in this behalf,—
(i) the capital gains arising from such conversion shall not be chargeable to tax in the assessment year relevant to the previous year in which such conversion takes place; (ii) the provisions of this Act relating to treatment of unabsorbed depreciation, set off or carry forward and set off of losses, tax credit in respect of tax paid on deemed income relating to certain companies and the computation of income in the case of the foreign company and Indian subsidiary company shall apply with such exceptions, modifications and adaptations as may be specified in that notification. (2) In case of failure to comply with any of the conditions specified in the scheme or in the notification issued under sub-section (1), all the provisions of this Act shall apply to the foreign company and the said Indian subsidiary company without any benefit, exemption or relief under sub-section (1). (3) Where, in a previous year, any benefit, exemption or relief has been claimed and granted to the foreign company or the Indian subsidiary company in accordance with the provisions of sub-section (1) and, subsequently, there is failure to comply with any of the conditions specified in the scheme or in the notification issued under sub-section (1), then,— (i) such benefit, exemption or relief shall be deemed to have been wrongly allowed; (ii) the Assessing Officer may, notwithstanding anything contained in this Act, re-compute the total income of the assessee for the said previous year and make the necessary amendment; and (iii) the provisions of section 154 shall, so far as may be, apply thereto and the period of four years specified in sub-section (7) of that section being reckoned from the end of the previous year in which the failure to comply with the condition referred to in sub-section (1) takes place. (4) Every notification issued under this section shall be laid before each House of Parliament. |

GST i.e.Goods and Service Tax is a unified tax that replaces several indirect taxesleviedby the Central Government and the State Government(s)....
Read more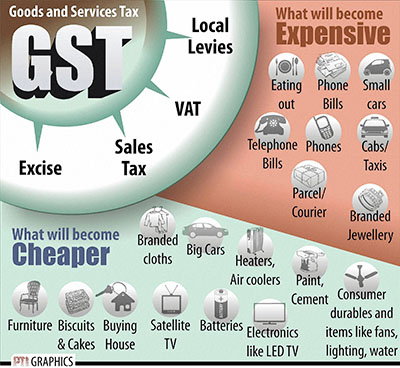
In pre-GST regime, goodswere liable to: (i) Excise Duty- on manufacture of goods; (ii) VAT/CST- on sale of goods; (iii) Entry tax- on ...
Read more
GST is levied on every taxable person. Taxable person means a person who carries on any business at any place in India. Such . ..
Read more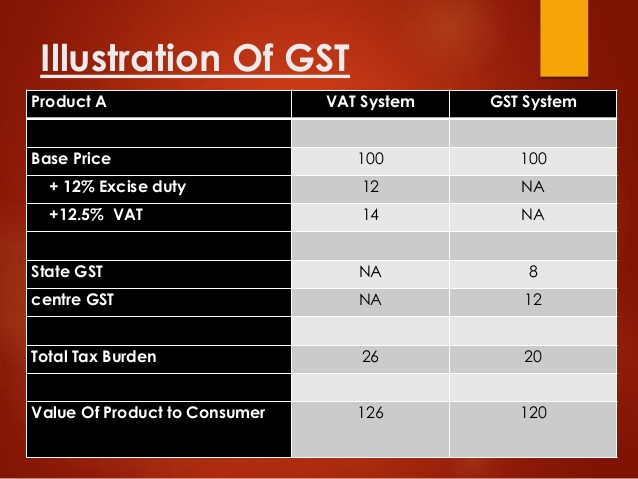
GST is a unified tax which is levied on: (i) goods; (ii) services and (iii) a mix of goods and/or services. Any supply of goods or services . .. ...
Read moreGST India Solution is an effort of firm of professionals who welcome implementation of GST. This is an interactiveplatformthat aspires to disseminate right knowledge to professionals, practitioners and public at large. This platform has beenfloatedbya firm of Chartered Accountants relentlessly working in field of direct and indirect taxes since early 1985.
READ MORE
Our core competence is statutory compliance, advisory, corporate tax planning and appellate matters of direct and indirect taxesandcorporate training sessions on GST.
The senior partner of the firm has to his credit several professional publications viz., Delhi Sales Tax Right to Use Goods Act, Delhi VAT, Maharashtra VAT, West Bengal VAT, Haryana VAT published by Taxmann. Madhya Pradesh VAT and Chhattisgarh VAT were published by Suvidha Law House, Bhopal. He has also addressed seminars on indirect taxes organized by professional bodies like ICAI, IMA, NIFM etc. and has also contributed articles on subjects of pro. . . . .