
WHAT IS GST?
GST i.e.Goods and Service Tax is a unified tax that replaces several indirect taxesleviedby the Central Government and the State Government(s)....
Read more|
92B. Meaning of international transaction.—(1) For the purposes of this section and sections 92, 92C, 92D and 92E, "international transaction" means a transaction between two or more associated enterprises, either or both of whom are non-residents, in the nature of purchase, sale or lease of tangible or intangible property, or provision of services, or lending or borrowing money, or any other transaction having a bearing on the profits, income, losses or assets of such enterprises, and shall include a mutual agreement or arrangement between two or more associated enterprises for the allocation or apportionment of, or any contribution to, any cost or expense incurred or to be incurred in connection with a benefit, service or facility provided or to be provided to any one or more of such enterprises.
(2) A transaction entered into by an enterprise with a person other than an associated enterprise shall, for the purposes of sub-section (1), be deemed to be an international transaction entered into between two associated enterprises, if there exists a prior agreement in relation to the relevant transaction between such other person and the associated enterprise, or the terms of the relevant transaction are determined in substance between such other person and the associated enterprise where the enterprise or the associated enterprise or both of them are non-residents irrespective of whether such other person is a non-resident or not. Explanation.—For the removal of doubts, it is hereby clarified that— (i) the expression "international transaction" shall include— (a) the purchase, sale, transfer, lease or use of tangible property including building, transportation vehicle, machinery, equipment, tools, plant, furniture, commodity or any other article, product or thing; (b) the purchase, sale, transfer, lease or use of intangible property, including the transfer of ownership or the provision of use of rights regarding land use, copyrights, patents, trademarks, licences, franchises, customer list, marketing channel, brand, commercial secret, know-how, industrial property right, exterior design or practical and new design or any other business or commercial rights of similar nature; (c) capital financing, including any type of long-term or short-term borrowing, lending or guarantee, purchase or sale of marketable securities or any type of advance, payments or deferred payment or receivable or any other debt arising during the course of business; (d) provision of services, including provision of market research, market development, marketing management, administration, technical service, repairs, design, consultation, agency, scientific research, legal or accounting service; (e) a transaction of business restructuring or reorganisation, entered into by an enterprise with an associated enterprise, irrespective of the fact that it has bearing on the profit, income, losses or assets of such enterprises at the time of the transaction or at any future date; (ii) the expression "intangible property" shall include— (a) marketing related intangible assets, such as, trademarks, trade names, brand names, logos; (b) technology related intangible assets, such as, process patents, patent applications, technical documentation such as laboratory notebooks, technical know-how; (c) artistic related intangible assets, such as, literary works and copyrights, musical compositions, copyrights, maps, engravings; (d) data processing related intangible assets, such as, proprietary computer software, software copyrights, automated databases, and integrated circuit masks and masters; (e) engineering related intangible assets, such as, industrial design, product patents, trade secrets, engineering drawing and schema-tics, blueprints, proprietary documentation; (f) customer related intangible assets, such as, customer lists, customer contracts, customer relationship, open purchase orders; (g) contract related intangible assets, such as, favourable supplier, contracts, licence agreements, franchise agreements, non-compete agreements; (h) human capital related intangible assets, such as, trained and organised work force, employment agreements, union contracts; (i) location related intangible assets, such as, leasehold interest, mineral exploitation rights, easements, air rights, water rights; (j) goodwill related intangible assets, such as, institutional goodwill, professional practice goodwill, personal goodwill of professional, celebrity goodwill, general business going concern value; (k) methods, programmes, systems, procedures, campaigns, surveys, studies, forecasts, estimates, customer lists, or technical data; (l) any other similar item that derives its value from its intellectual content rather than its physical attributes. |

GST i.e.Goods and Service Tax is a unified tax that replaces several indirect taxesleviedby the Central Government and the State Government(s)....
Read more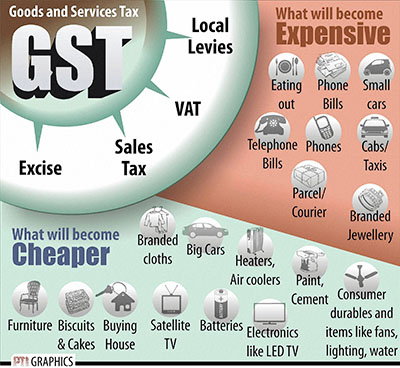
In pre-GST regime, goodswere liable to: (i) Excise Duty- on manufacture of goods; (ii) VAT/CST- on sale of goods; (iii) Entry tax- on ...
Read more
GST is levied on every taxable person. Taxable person means a person who carries on any business at any place in India. Such . ..
Read more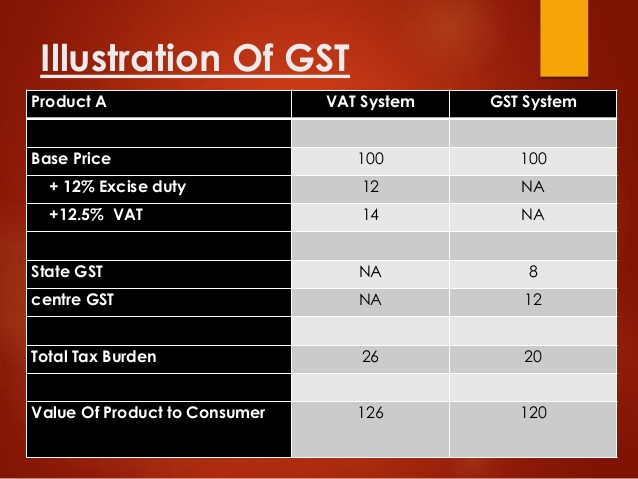
GST is a unified tax which is levied on: (i) goods; (ii) services and (iii) a mix of goods and/or services. Any supply of goods or services . .. ...
Read moreGST India Solution is an effort of firm of professionals who welcome implementation of GST. This is an interactiveplatformthat aspires to disseminate right knowledge to professionals, practitioners and public at large. This platform has beenfloatedbya firm of Chartered Accountants relentlessly working in field of direct and indirect taxes since early 1985.
READ MORE
Our core competence is statutory compliance, advisory, corporate tax planning and appellate matters of direct and indirect taxesandcorporate training sessions on GST.
The senior partner of the firm has to his credit several professional publications viz., Delhi Sales Tax Right to Use Goods Act, Delhi VAT, Maharashtra VAT, West Bengal VAT, Haryana VAT published by Taxmann. Madhya Pradesh VAT and Chhattisgarh VAT were published by Suvidha Law House, Bhopal. He has also addressed seminars on indirect taxes organized by professional bodies like ICAI, IMA, NIFM etc. and has also contributed articles on subjects of pro. . . . .