
WHAT IS GST?
GST i.e.Goods and Service Tax is a unified tax that replaces several indirect taxesleviedby the Central Government and the State Government(s)....
Read more|
CHAPTER VI REGISTRATION 22. Persons liable for registration. (1) Every supplier shall be liable to be registered under this Act in the State or Union territory, other than special category States, from where he makes a taxable supply of goods or services or both, if his aggregate turnover in a financial year exceeds twenty lakh rupees: Provided that where such person makes taxable supplies of goods or services or both from any of the special category States, he shall be liable to be registered if his aggregate turnover in a financial year exceeds ten lakh rupees. (2) Every person who, on the day immediately preceding the appointed day, is registered or holds a licence under an existing law, shall be liable to be registered under this Act with effect from the appointed day. (3) Where a business carried on by a taxable person registered under this Act is transferred, whether on account of succession or otherwise, to another person as a going concern, the transferee or the successor, as the case may be, shall be liable to be registered with effect from the date of such transfer or succession. (4) Notwithstanding anything contained in sub-sections (1) and (3), in a case of transfer pursuant to sanction of a scheme or an arrangement for amalgamation or, as the case may be, demerger of two or more companies pursuant to an order of a High Court, Tribunal or otherwise, the transferee shall be liable to be registered, with effect from the date on which the Registrar of Companies issues a certificate of incorporation giving effect to such order of the High Court or Tribunal. Explanation.––For the purposes of this section,–– (i) the expression “aggregate turnover” shall include all supplies made by the taxable person, whether on his own account or made on behalf of all his principals; (ii) the supply of goods, after completion of job work, by a registered job worker shall be treated as the supply of goods by the principal referred to in section 143, and the value of such goods shall not be included in the aggregate turnover of the registered job worker; (iii) the expression “special category States” shall mean the States as specified in sub-clause (g) of clause (4) of article 279A of the Constitution.
23. Persons not liable for registration. (1) The following persons shall not be liable to registration, namely:–– (a) any person engaged exclusively in the business of supplying goods or services or both that are not liable to tax or wholly exempt from tax under this Act or under the Integrated Goods and Services Tax Act; (b) an agriculturist, to the extent of supply of produce out of cultivation of land. (2) The Government may, on the recommendations of the Council, by notification, specify the category of persons who may be exempted from obtaining registration under this Act.
24. Compulsory registration in certain cases Notwithstanding anything contained in sub-section (1) of section 22, the following categories of persons shall be required to be registered under this Act,–– (i) persons making any inter-State taxable supply; (ii) casual taxable persons making taxable supply; (iii) persons who are required to pay tax under reverse charge; (iv) person who are required to pay tax under sub-section (5) of section 9; (v) non-resident taxable persons making taxable supply; (vi) persons who are required to deduct tax under section 51, whether or not separately registered under this Act; (vii) persons who make taxable supply of goods or services or both on behalf of other taxable persons whether as an agent or otherwise; (viii) Input Service Distributor, whether or not separately registered under this Act; (ix) persons who supply goods or services or both, other than supplies specified under sub-section (5) of section 9, through such electronic commerce operator who is required to collect tax at source under section 52; (x) every electronic commerce operator; (xi) every person supplying online information and database access or retrieval services from a place outside India to a person in India, other than a registered person; and (xii) such other person or class of persons as may be notified by the Government on the recommendations of the Council.
25. Procedure for registration. (1) Every person who is liable to be registered under section 22 or section 24 shall apply for registration in every such State or Union territory in which he is so liable within thirty days from the date on which he becomes liable to registration, in such manner and subject to such conditions as may be prescribed: Provided that a casual taxable person or a non-resident taxable person shall apply for registration at least five days prior to the commencement of business. Explanation.—Every person who makes a supply from the territorial waters of India shall obtain registration in the coastal State or Union territory where the nearest point of the appropriate baseline is located. (2) A person seeking registration under this Act shall be granted a single registration in a State or Union territory: Provided that a person having multiple business verticals in a State or Union territory may be granted a separate registration for each business vertical, subject to such conditions as may be prescribed. (3) A person, though not liable to be registered under section 22 or section 24 may get himself registered voluntarily, and all provisions of this Act, as are applicable to a registered person, shall apply to such person. (4) A person who has obtained or is required to obtain more than one registration, whether in one State or Union territory or more than one State or Union territory shall, in respect of each such registration, be treated as distinct persons for the purposes of this Act. (5) Where a person who has obtained or is required to obtain registration in a State or Union territory in respect of an establishment, has an establishment in another State or Union territory, then such establishments shall be treated as establishments of distinct persons for the purposes of this Act. (6) Every person shall have a Permanent Account Number issued under the Incometax Act, 1961 in order to be eligible for grant of registration: Provided that a person required to deduct tax under section 51 may have, in lieu of a Permanent Account Number, a Tax Deduction and Collection Account Number issued under the said Act in order to be eligible for grant of registration. (7) Notwithstanding anything contained in sub-section (6), a non-resident taxable person may be granted registration under sub-section (1) on the basis of such other documents as may be prescribed. (8) Where a person who is liable to be registered under this Act fails to obtain registration, the proper officer may, without prejudice to any action which may be taken under this Act or under any other law for the time being in force, proceed to register such person in such manner as may be prescribed. (9) Notwithstanding anything contained in sub-section (1),–– (a) any specialised agency of the United Nations Organisation or any Multilateral Financial Institution and Organisation notified under the United Nations (Privileges and Immunities) Act, 1947, Consulate or Embassy of foreign countries; and (b) any other person or class of persons, as may be notified by the Commissioner, shall be granted a Unique Identity Number in such manner and for such purposes, including refund of taxes on the notified supplies of goods or services or both received by them, as may be prescribed. (10) The registration or the Unique Identity Number shall be granted or rejected after due verification in such manner and within such period as may be prescribed. (11) A certificate of registration shall be issued in such form and with effect from such date as may be prescribed. (12) A registration or a Unique Identity Number shall be deemed to have been granted after the expiry of the period prescribed under sub-section (10), if no deficiency has been communicated to the applicant within that period.
26.Deemed registration. (1) The grant of registration or the Unique Identity Number under the State Goods and Services Tax Act or the Union Territory Goods and Services Tax Act shall be deemed to be a grant of registration or the Unique Identity Number under this Act subject to the condition that the application for registration or the Unique Identity Number has not been rejected under this Act within the time specified in sub-section (10) of section 25. (2) Notwithstanding anything contained in sub-section (10) of section 25, any rejection of application for registration or the Unique Identity Number under the State Goods and Services Tax Act or the Union Territory Goods and Services Tax Act shall be deemed to be a rejection of application for registration under this Act.
27. Special provisions relating to casual taxable person and non-resident taxable person. (1) The certificate of registration issued to a casual taxable person or a nonresident taxable person shall be valid for the period specified in the application for registration or ninety days from the effective date of registration, whichever is earlier and such person shall make taxable supplies only after the issuance of the certificate of registration: Provided that the proper officer may, on sufficient cause being shown by the said taxable person, extend the said period of ninety days by a further period not exceeding ninety days. (2) A casual taxable person or a non-resident taxable person shall, at the time of submission of application for registration under sub-section (1) of section 25, make an advance deposit of tax in an amount equivalent to the estimated tax liability of such person for the period for which the registration is sought: Provided that where any extension of time is sought under sub-section (1), such taxable person shall deposit an additional amount of tax equivalent to the estimated tax liability of such person for the period for which the extension is sought. (3) The amount deposited under sub-section (2) shall be credited to the electronic cash ledger of such person and shall be utilised in the manner provided under section 49.
28. Amendment of registration. (1) Every registered person and a person to whom a Unique Identity Number has been assigned shall inform the proper officer of any changes in the information furnished at the time of registration or subsequent thereto, in such form and manner and within such period as may be prescribed. (2) The proper officer may, on the basis of information furnished under sub-section (1) or as ascertained by him, approve or reject amendments in the registration particulars in such manner and within such period as may be prescribed: Provided that approval of the proper officer shall not be required in respect of amendment of such particulars as may be prescribed: Provided further that the proper officer shall not reject the application for amendment in the registration particulars without giving the person an opportunity of being heard. (3) Any rejection or approval of amendments under the State Goods and Services Tax Act or the Union Territory Goods and Services Tax Act, as the case may be, shall be deemed to be a rejection or approval under this Act.
29. Cancellation of registration. (1) The proper officer may, either on his own motion or on an application filed by the registered person or by his legal heirs, in case of death of such person, cancel the registration, in such manner and within such period as may be prescribed, having regard to the circumstances where,–– (a) the business has been discontinued, transferred fully for any reason including death of the proprietor, amalgamated with other legal entity, demerged or otherwise disposed of; or (b) there is any change in the constitution of the business; or (c) the taxable person, other than the person registered under sub-section (3) of section 25, is no longer liable to be registered under section 22 or section 24. (2) The proper officer may cancel the registration of a person from such date, including any retrospective date, as he may deem fit, where,–– (a) a registered person has contravened such provisions of the Act or the rules made thereunder as may be prescribed; or (b) a person paying tax under section 10 has not furnished returns for three consecutive tax periods; or (c) any registered person, other than a person specified in clause (b), has not furnished returns for a continuous period of six months; or (d) any person who has taken voluntary registration under sub-section (3) of section 25 has not commenced business within six months from the date of registration; or (e) registration has been obtained by means of fraud, wilful misstatement or suppression of facts: Provided that the proper officer shall not cancel the registration without giving the person an opportunity of being heard. (3) The cancellation of registration under this section shall not affect the liability of the person to pay tax and other dues under this Act or to discharge any obligation under this Act or the rules made thereunder for any period prior to the date of cancellation whether or not such tax and other dues are determined before or after the date of cancellation. (4) The cancellation of registration under the State Goods and Services Tax Act or the Union Territory Goods and Services Tax Act, as the case may be, shall be deemed to be a cancellation of registration under this Act. (5) Every registered person whose registration is cancelled shall pay an amount, by way of debit in the electronic credit ledger or electronic cash ledger, equivalent to the credit of input tax in respect of inputs held in stock and inputs contained in semi-finished or finished goods held in stock or capital goods or plant and machinery on the day immediately preceding the date of such cancellation or the output tax payable on such goods, whichever is higher, calculated in such manner as may be prescribed: Provided that in case of capital goods or plant and machinery, the taxable person shall pay an amount equal to the input tax credit taken on the said capital goods or plant and machinery, reduced by such percentage points as may be prescribed or the tax on the transaction value of such capital goods or plant and machinery under section 15, whichever is higher. (6) The amount payable under sub-section (5) shall be calculated in such manner as may be prescribed.
30. Revocation of cancellation of registration. (1) Subject to such conditions as may be prescribed, any registered person, whose registration is cancelled by the proper officer on his own motion, may apply to such officer for revocation of cancellation of the registration in the prescribed manner within thirty days from the date of service of the cancellation order. (2) The proper officer may, in such manner and within such period as may be prescribed, by order, either revoke cancellation of the registration or reject the application: Provided that the application for revocation of cancellation of registration shall not be rejected unless the applicant has been given an opportunity of being heard. (3) The revocation of cancellation of registration under the State Goods and Services Tax Act or the Union Territory Goods and Services Tax Act, as the case may be, shall be deemed to be a revocation of cancellation of registration under this Act. |

GST i.e.Goods and Service Tax is a unified tax that replaces several indirect taxesleviedby the Central Government and the State Government(s)....
Read more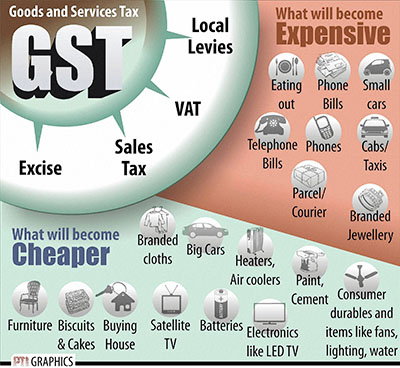
In pre-GST regime, goodswere liable to: (i) Excise Duty- on manufacture of goods; (ii) VAT/CST- on sale of goods; (iii) Entry tax- on ...
Read more
GST is levied on every taxable person. Taxable person means a person who carries on any business at any place in India. Such . ..
Read more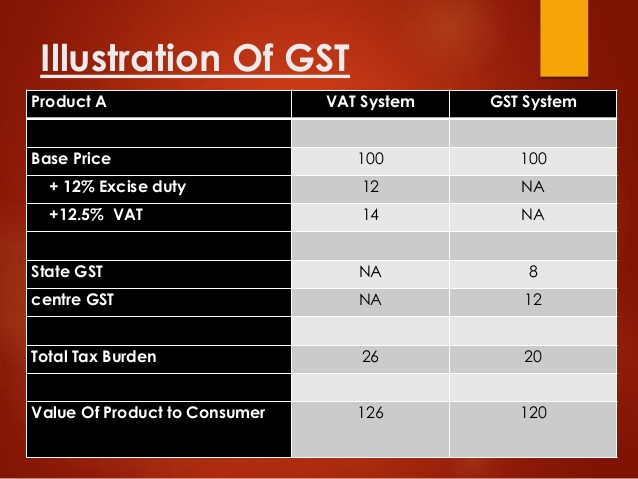
GST is a unified tax which is levied on: (i) goods; (ii) services and (iii) a mix of goods and/or services. Any supply of goods or services . .. ...
Read moreGST India Solution is an effort of firm of professionals who welcome implementation of GST. This is an interactiveplatformthat aspires to disseminate right knowledge to professionals, practitioners and public at large. This platform has beenfloatedbya firm of Chartered Accountants relentlessly working in field of direct and indirect taxes since early 1985.
READ MORE
Our core competence is statutory compliance, advisory, corporate tax planning and appellate matters of direct and indirect taxesandcorporate training sessions on GST.
The senior partner of the firm has to his credit several professional publications viz., Delhi Sales Tax Right to Use Goods Act, Delhi VAT, Maharashtra VAT, West Bengal VAT, Haryana VAT published by Taxmann. Madhya Pradesh VAT and Chhattisgarh VAT were published by Suvidha Law House, Bhopal. He has also addressed seminars on indirect taxes organized by professional bodies like ICAI, IMA, NIFM etc. and has also contributed articles on subjects of pro. . . . .