
WHAT IS GST?
GST i.e.Goods and Service Tax is a unified tax that replaces several indirect taxesleviedby the Central Government and the State Government(s)....
Read more|
CHAPTER VI
ADJUDICATION OF DISPUTE AND CLAIMS
74. Constitution of Employees’ Insurance Court. —(1) The 1[State] Government shall, by notification in the Official Gazette, constitute an Employees’ Insurance Court for such local area as may be specified in the notification. (2) The Court shall consist of such number of judges as the 1[State] Government may think fit. (3) Any person who is or has been a judicial officer or is a legal practitioner of five years’ standing shall be qualified to be a Judge of the Employees’ Insurance Court. (4) The 1[State] Government may appoint the same Court for two or more local areas or two or more Courts for the same local area. (5) Where more than one Court has been appointed for the same local area, the 1[State] Government may by general or special order regulate the distribution of business between them.
75. Matters to be decided by the Employees’ Insurance Court. — (1) If any question or dispute arises as to — (a) whether any person is an employee within the meaning of this Act or whether he is liable to pay the employee’s contribution, or (b) the rate of wages or average daily wages of an employee for the purposes of this Act, or (c) the rate of contribution payable by a principal employer in respect of any employee, or (d) the person who is or was the principal employer in respect of any employee, or (e) the right of any person to any benefit and as to the amount and duration thereof, or 1[(ee) any direction issued by the Corporation under section 55-A on a review of any payment of dependants’ benefits, or] 2[(f) * * *] (g) any other matter which is in dispute between a principal employer and the Corporation, or between a principal employer and an immediate employer, or between a person and the Corporation or between an employee and a principal or immediate employer, in respect of any contribution or benefit or other dues payable or recoverable under this Act, 3[or any other matter required to be or which may be decided by the Employees’ Insurance Court under this Act], such question or dispute 4[subject to the provisions of sub-section (2A)] shall be decided by the Employees’ Insurance Court in accordance with the provisions of this Act. (2) 5[Subject to the provisions of sub-section (2A), the following claims] shall be decided by the Employees’ Insurance Court, namely : — (a) claim for the recovery of contribution from the principal employer ; (b) claim by a principal employer to recover contributions from any immediate employer ; 1[(c) * * *] (d) claim against a principal employer under section 68 ; (e) claim under section 70 for the recovery of the value or amount of the benefits received by a person when he is not lawfully entitled thereto ; and (f) If any claim for the recovery of any benefit admissible under this Act. 2[(2A) If in any proceedings before the Employees’ Insurance Court a disablement question arises and the decision of a medical board or a medical appeal tribunal has not been obtained on the same and the decision of such question is necessary for the determination of the claim or question before the Employees’ Insurance Court, that Court shall direct the Corporation to have the question decided by this Act and shall thereafter proceed with the determination of the claim or question before it in accordance with the decision of the medical board or the medical appeal tribunal, as the case may be, except where an appeal has been filed before the Employees’ Insurance Court under sub-section (2) of section 54-A in which case the Employees’ Insurance Court may itself determine all the issues arising before it.] 3[(2-B) No matter which is in dispute between a principal employer and the Corporation in respect of any contribution or any other dues shall be raised by the principal employer in the Employees’ Insurance Court unless he has deposited with the Court fifty per cent. of the amount due from him as claimed by the Corporation : Provided that the Court may, for reasons to be recorded in writing, waive or reduce the amount to be deposited under this sub-section.] (3) No civil Court shall have jurisdiction to decide or deal with any question or dispute as aforesaid or to adjudicate on any liability which by or under this Act is to be decided by 1[a medical board, or by a medical appeal tribunal or by the Employees’ Insurance Court].
76. Institution of proceedings, etc. — (1) Subject to the provisions of this Act and any rules made by the 2[State] Government, all proceedings before the Employees’ Insurance Court shall be instituted in the Court appointed for the local area in which the insured person was working at the time the question or dispute arose. (2) If the Court is satisfied that any matter arising out of any proceedings pending before it can be more conveniently dealt with by any other Employees’ Insurance Court in the same 3[State], it may, subject to any rules made by the 2[State] Government in this behalf, order such matter to be transferred to such other Court for disposal and shall forthwith transmit to such other Court the records connected with that matter. (3) The 2[State] Government may transfer any matter pending before any Employees’ Insurance Court in the 3[State] to any such Court in another 3[State] with the consent of the 2[State] Government of that State. (4) The Court to which any matter is transferred under sub-section (2) or sub-section (3) shall continue the proceedings as if they had been originally instituted in it.
77. Commencement of proceedings. — (1) The proceeding before an Employees’ Insurance Court shall be commenced by application. 4[(1-A) Every such application shall be made within a period of three years from the date on which the cause of action arose. Explanation.— For the purpose of this sub-section, — (a) the cause of action in respect of a claim for benefit shall not be deemed to arise unless the insured person or in the case of dependants’ benefit, the dependants of the insured person claims or claim that benefit in accordance with the regu-lations made in that behalf within a period of twelve months after the claim became due or within such further period as the Employees’ Insurance Court may allow on grounds which appear to it to be reasonable ; 1[(b) the cause of action in respect of a claim by the Corpo-ration for recovering contributions (including interest and damages) from the principal employer shall be deemed to have arisen on the date on which such claim is made by the Corporation for the first time : Provided that no claim shall be made by the Corporation after five years of the period to which the claim relates ; (c) the cause of action in respect of a claim by the principal employer for recovering contributions from an immediate employer shall not be deemed to arise till the date by which the evidence of contributions having been paid is due to be received by the Corporation under the regulations.].] (2) Every such application shall be in such form and shall contain such particulars and shall be accompanied by such fee if any, as may be prescribed by rules made by the State Government in consultation with the Corporation.
78. Powers of Employees’ Insurance Court. — (1) The Employees’ Insurance Court shall have all the powers of a civil Court for the purposes of summoning and enforcing the attendance of witnesses, compelling the discovery and production of documents and material objects, administering oath and recording evidence and such Court shall be deemed to be a civil Court within the meaning of 1[section 195 and Chapter XXVI of the Code of Criminal Procedure, 1973 (2 of 1974)]. (2) The Employees’ Insurance Court shall follow such procedure as may be prescribed by rules made by the 2[State] Government. (3) All costs incidental to any proceeding before an Employees’ Insurance Court shall, subject to such rules as may be made in this behalf by the 2[State] Government, be in the discretion of the Court. (4) An order of the Employees’ Insurance Court shall be enforceable as if it were a decree passed in a suit by a civil Court.
79. Appearance by legal practitioners, etc. — Any application, appearance or act required to be made or done by any person to or before an Employees’ Insurance Court (other than appearance of a person required for the purpose of this examination as a witness) may be made or done by a legal practitioner or by an officer of a registered trade union authorised in writing by such person or, with the permission of the Court, by any other person so authorised.
3[80. Benefit not admissible unless claimed in time.— * * *]
81. Reference to High Court. — An Employees’ Insurance Court may submit any question of law for the decision of the High Court and if does so shall decide the question pending before it in accordance with such decision.
82. Appeal. — (1) Save as expressly provided in this section, no appeal shall lie from an order of an Employees’ Insurance Court. (2) An appeal shall lie to the High Court from an order of an Employees’ Insurance Court if it involves a substantial question of law. (3) The period of limitation for an appeal under this section shall be sixty days. (4) The provisions of sections 5 and 12 of the 1[Limitation Act, 1963 (36 of 1963)] shall apply to appeals under this section.
83. Stay of payment pending appeal. — Where the Corporation has presented an appeal against an order of the Employees’ Insurance Court, that Court may, and if so directed by the High Court shall, pending the decision of the appeal, withhold the payment of any sum directed to be paid by the order appealed against.
|

GST i.e.Goods and Service Tax is a unified tax that replaces several indirect taxesleviedby the Central Government and the State Government(s)....
Read more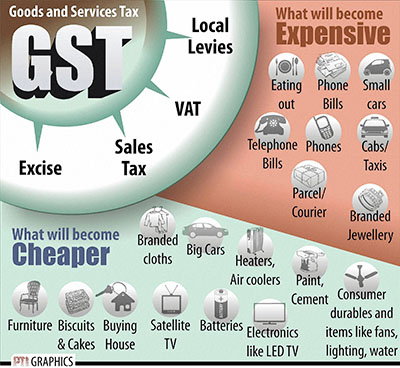
In pre-GST regime, goodswere liable to: (i) Excise Duty- on manufacture of goods; (ii) VAT/CST- on sale of goods; (iii) Entry tax- on ...
Read more
GST is levied on every taxable person. Taxable person means a person who carries on any business at any place in India. Such . ..
Read more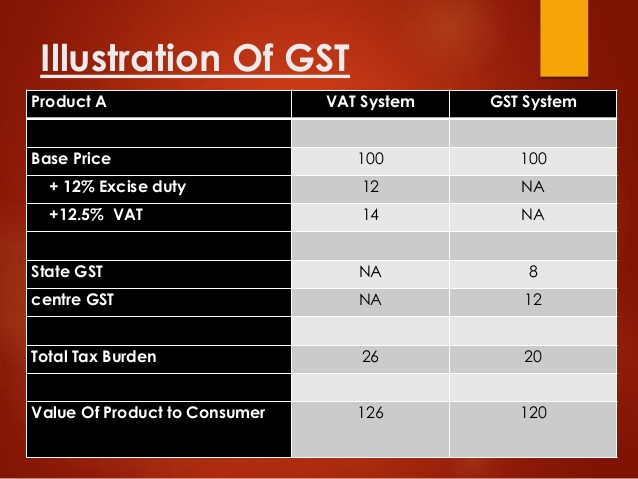
GST is a unified tax which is levied on: (i) goods; (ii) services and (iii) a mix of goods and/or services. Any supply of goods or services . .. ...
Read moreGST India Solution is an effort of firm of professionals who welcome implementation of GST. This is an interactiveplatformthat aspires to disseminate right knowledge to professionals, practitioners and public at large. This platform has beenfloatedbya firm of Chartered Accountants relentlessly working in field of direct and indirect taxes since early 1985.
READ MORE
Our core competence is statutory compliance, advisory, corporate tax planning and appellate matters of direct and indirect taxesandcorporate training sessions on GST.
The senior partner of the firm has to his credit several professional publications viz., Delhi Sales Tax Right to Use Goods Act, Delhi VAT, Maharashtra VAT, West Bengal VAT, Haryana VAT published by Taxmann. Madhya Pradesh VAT and Chhattisgarh VAT were published by Suvidha Law House, Bhopal. He has also addressed seminars on indirect taxes organized by professional bodies like ICAI, IMA, NIFM etc. and has also contributed articles on subjects of pro. . . . .