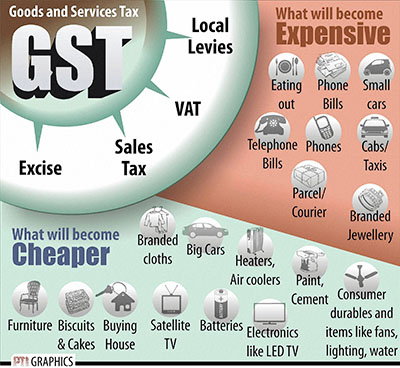
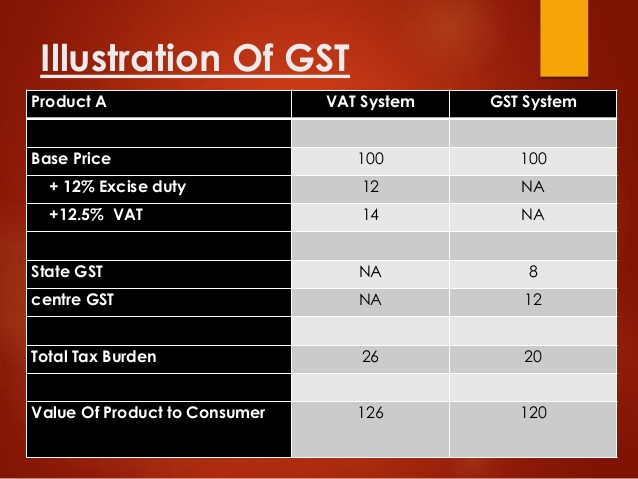
|
|
(1)
|
|
Every public authority shall—
|
|
|
|
(a)
|
maintain all its records duly catalogued and indexed in a manner and the form which facilitates the right to information under this Act and ensure that all records that are appropriate to be computerised are, within a reasonable time and subject to availability of resources, computerised and connected through a network all over the country on different systems so that access to such records is facilitated;
|
|
|
|
(b)
|
publish within one hundred and twenty days from the enactment of this Act,—
|
|
|
|
|
(i)
|
the particulars of its organisation, functions and duties;
|
|
|
|
|
(ii)
|
the powers and duties of its officers and employees;
|
|
|
|
|
(iii)
|
the procedure followed in the decision making process, including channels of supervision and accountability;
|
|
|
|
|
(iv)
|
the norms set by it for the discharge of its functions;
|
|
|
|
|
(v)
|
the rules, regulations, instructions, manuals and records, held by it or under its control or used by its employees for discharging its functions;
|
|
|
|
|
(vi)
|
a statement of the categories of documents that are held by it or under its control;
|
|
|
|
|
(vii)
|
the particulars of any arrangement that exists for consultation with, or representation by, the members of the public in relation to the formulation of its policy or implementation thereof;
|
|
|
|
|
(viii)
|
a statement of the boards, councils, committees and other bodies consisting of two or more persons constituted as its part or for the purpose of its advice, and as to whether meetings of those boards, councils, committees and other bodies are open to the public, or the minutes of such meetings are accessible for public;
|
|
|
|
|
(ix)
|
a directory of its officers and employees;
|
|
|
|
|
(x)
|
the monthly remuneration received by each of its officers and employees, including the system of compensation as provided in its regulations;
|
|
|
|
|
(xi)
|
the budget allocated to each of its agency, indicating the particulars of all plans, proposed expenditures and reports on disbursements made;
|
|
|
|
|
(xii)
|
the manner of execution of subsidy programmes, including the amounts allocated and the details of beneficiaries of such programmes;
|
|
|
|
|
(xiii)
|
particulars of recipients of concessions, permits or authorisations granted by it;
|
|
|
|
|
(xiv)
|
details in respect of the information, available to or held by it, reduced in an electronic form;
|
|
|
|
|
(xv)
|
the particulars of facilities available to citizens for obtaining information, including the working hours of a library or reading room, if maintained for public use;
|
|
|
|
|
(xvi)
|
the names, designations and other particulars of the Public Information Officers;
|
|
|
|
|
(xvii)
|
such other information as may be prescribed and thereafter update these publications every year;
|
|
|
|
(c)
|
publish all relevant facts while formulating important policies or announcing the decisions which affect public;
|
|
|
|
(d)
|
provide reasons for its administrative or quasi-judicial decisions to affected persons.
|
|
|
(2)
|
|
It shall be a constant endeavour of every public authority to take steps in accordance with the requirements of clause (b) of sub-section (1) to provide as much information suo motu to the public at regular intervals through various means of communications, including internet, so that the public have minimum resort to the use of this Act to obtain information.
|
|
|
(3)
|
|
For the purposes of sub-section (1), every information shall be disseminated widely and in such form and manner which is easily accessible to the public.
|
|
|
(4)
|
|
All materials shall be disseminated taking into consideration the cost effectiveness, local language and the most effective method of communication in that local area and the information should be easily accessible, to the extent possible in electronic format with the Central Public Information Officer or State Public Information Officer, as the case may be, available free or at such cost of the medium or the print cost price as may be prescribed.
|
|
|
|
|
Explanation.—For the purposes of sub-sections (3) and (4), "disseminated" means making known or communicated the information to the public through notice boards, newspapers, public announcements, media broadcasts, the internet or any other means, including inspection of offices of any public authority.
|