
WHAT IS GST?
GST i.e.Goods and Service Tax is a unified tax that replaces several indirect taxesleviedby the Central Government and the State Government(s)....
Read more|
2. Definitions.- In this Act, unless the context otherwise requires,- (a) “appropriate Government” means,- (i) in relation to an establishment:- (a) belonging to, or under the control of, the Central Government (b) having branches in more than one State (c) of a factory belonging to, or under the control of, the Central Government. (d) of a major port, mine, oilfield or railway company, the Central Government. (ii) in any other case, the State Government. (b) “completed year of service” means continuous service for one year. (c) “continuous service” means continuous service as defined in Section 2-A (d) “controlling Authority” means an authority appointed by the appropriate Government under Section 3; (e) “employee” means any person (other than an apprentice) who is employed for wages, whether the terms of such employment are express or implied, in any kind of work, manual or otherwise, in or in connection with the work of a factory, mine, oilfield, plantation, port, railway company, shop or other establishment to which this Act applies, but does not include any such person who holds a post under the Central Government or a State Government and is governed by any other Act or by any rules providing for payment of gratuity; (f) “Employer” means, in relation to any establishment, factory, mine, oilfield, plantation, port, railway company or shop:- (i) belonging to, or under the control of, the Central Government or a State Government, a person or authority appointed by the appropriate Government for the supervision and control of employees, or where no person or authority has been so appointed, the head of the Ministry or the Department concerned, (ii) belonging to, or under the control of, any local authority, the person appointed by such authority for the supervision and control of employees or where no person has been so appointed, the chief executive officer of the local authority. (iii) in any other case, the person, who, or the authority which, has the ultimate control over the affairs of the establishment, factory, mine, oilfield, plantation, port, railway company or shop, and where the said affairs are entrusted to any other person, whether called a manager, or managing director or by any other name, such person; (g) “Factory” has the meaning assigned to it in clause (m) of section 2 of the Factories Act, 1948 (63 of 1948); (h) “Family”, in relation to an employee, shall be deemed to consist of:- (i) in the case of a male employee, himself, his wife, his children, whether married or unmarried, his dependent parents [and the dependent parents of his wife and the widow] and children of his predeceased son, if any. (ii) in the case of a female employee, herself, her husband, her children, whether married or unmarried, her dependent parents and the dependent parents of her husband and the widow and children of her predeceased son, if any: Explanation.-Where the personal law of an employee permits the adoption by him of a child, any child lawfully adopted by him shall be deemed to be included in his family, and where a child of an employee has been adopted by another person and such adoption is, under the personal law of the person making such adoption, lawful, such child shall be deemed to be excluded from the family of the employee. (i) “major port” has the meaning assigned to it in clause (8) of section 3 of the Indian Ports Act, 1908 (15 of 1908); (j) “mine” has the meaning assigned to it in clause (j) of sub-section (1) of section 2 of the Mines Act, 1952 (35 of 1952); (k) “notification” means a notification published in the Official Gazette: (l) “oilfield” has the meaning assigned to it in clause (e) of Section 3 of the Oilfields (Regulation and Development) Act, 1948 (53 of 1948); (m) “plantation” has the meaning assigned to it in clause (f) of Section 2 of the Plantations Labour Act, 1951 (69 of 1951); (n) “port” has the meaning assigned to it in clause (4) of section 3 of the Indian Ports Act, 1908 (15 of 1908); (o) “prescribed” means prescribed by rules made under this Act; (p) “railway company” has the meaning assigned to it in clause (5) of section 3 of the Indian Railways Act, 1890 (9 of 1890); (q) “retirement” means termination of the service of an employee otherwise than on superannuation. (r) “superannuation” in relation to an employee, means the attainment by the employee of such age as is fixed in the contract or conditions of service as the age on the attainment of which the employer shall vacate the employment; (s) “wages” means all emoluments which are earned by an employee while on duty or on leave in accordance with the terms and conditions of his employment and which are paid or are payable to him in cash and includes dearness allowance but does not include any bonus, commission, house rent allowance, overtime wages and any other allowance. |

GST i.e.Goods and Service Tax is a unified tax that replaces several indirect taxesleviedby the Central Government and the State Government(s)....
Read more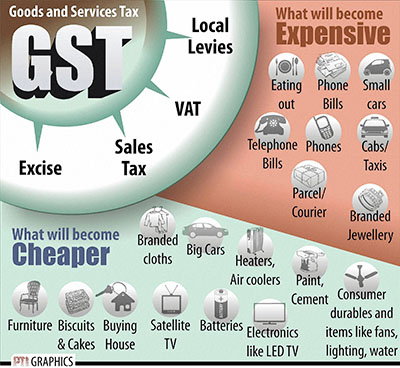
In pre-GST regime, goodswere liable to: (i) Excise Duty- on manufacture of goods; (ii) VAT/CST- on sale of goods; (iii) Entry tax- on ...
Read more
GST is levied on every taxable person. Taxable person means a person who carries on any business at any place in India. Such . ..
Read more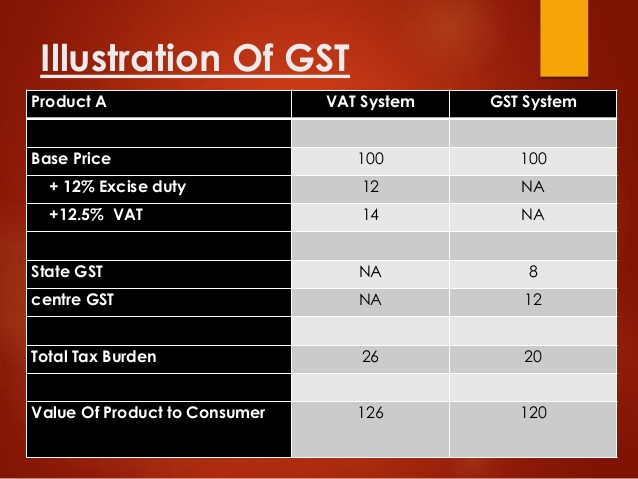
GST is a unified tax which is levied on: (i) goods; (ii) services and (iii) a mix of goods and/or services. Any supply of goods or services . .. ...
Read moreGST India Solution is an effort of firm of professionals who welcome implementation of GST. This is an interactiveplatformthat aspires to disseminate right knowledge to professionals, practitioners and public at large. This platform has beenfloatedbya firm of Chartered Accountants relentlessly working in field of direct and indirect taxes since early 1985.
READ MORE
Our core competence is statutory compliance, advisory, corporate tax planning and appellate matters of direct and indirect taxesandcorporate training sessions on GST.
The senior partner of the firm has to his credit several professional publications viz., Delhi Sales Tax Right to Use Goods Act, Delhi VAT, Maharashtra VAT, West Bengal VAT, Haryana VAT published by Taxmann. Madhya Pradesh VAT and Chhattisgarh VAT were published by Suvidha Law House, Bhopal. He has also addressed seminars on indirect taxes organized by professional bodies like ICAI, IMA, NIFM etc. and has also contributed articles on subjects of pro. . . . .