
WHAT IS GST?
GST i.e.Goods and Service Tax is a unified tax that replaces several indirect taxesleviedby the Central Government and the State Government(s)....
Read more|
78. Power to take action (1) A person who- (a) fails to comply with any provision of this Act or its regulations; or (b) fails to comply with or give effect to any notice, circular, guideline or practice note issued by the Registrar, commits a breach. (2) if a person has committed a breach and the Registrar is satisfied that it is appropriate in all the circumstances to take action against that person, the Registrar may take any one or more of the following actions: (a) direct the person in breach to comply with or give effect regulations, notices, to such provisions of the Act, circulars, guidelines or practice notes; (b) impose an administrative penalty, in proportion to the severity or gravity of the breach, but in any event not exceeding ten thousand ringgit; (c) reprimand the person in breach; or (d) direct the person in breach to take such steps to remedy the breach or to mitigate the effect of such breach, including making restitution to any person aggrieved by such breach.
(3) The Registrar shall give a written notice to a person in breach of his intention to take action under subsection (2) and shall give the person in breach an opportunity to be heard prior to him taking any action under subsection (2).
(4) if the Registrar considers that the limited liability partnership or any of its partners has failed to comply with the direction given under paragraph (2)(a) or (d), he may apply to the court for one or more of the following orders:
(a) an order directing the limited liability partnership or its partners to comply with the direction;
(b) an order directing the limited liability partnership or its partners to pay any costs incurred by the Registrar or other person relating to the issue of the direction by the Registrar or the breach of this Act or its regulations, notices, circulars, guidelines or practice notes relevant to the issue of the direction; or
(c) any other order that the court considers appropriate.
(5) Where a person has failed to pay an administrative penalty imposed by the Registrar under paragraph (2)(b), the administrative penalty imposed by the Registrar may be sued for and recovered as a civil debt due to the Registrar.
(6) For the purpose of paragraph (2)(d), in determining whether or not restitution is to be made by a person in breach, the Registrar shall have regard to-
(a) the profits that have accrued to such person in breach; or
(b) whether one or more persons have suffered loss or been otherwise adversely affected as a result of the breach.
(7) Nothing in this section prejudices the operation of any section imposing penalties on a limited liability partnership or its partners in respect of any failure under subsection (1), nor any powers that the Registrar or other person or the court may have under this Act.
|

GST i.e.Goods and Service Tax is a unified tax that replaces several indirect taxesleviedby the Central Government and the State Government(s)....
Read more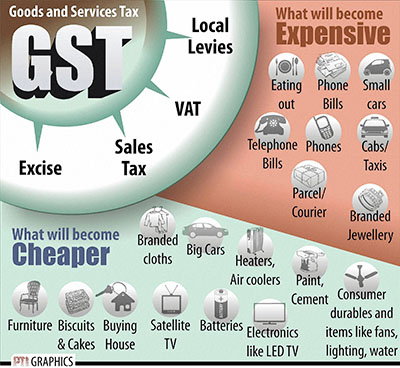
In pre-GST regime, goodswere liable to: (i) Excise Duty- on manufacture of goods; (ii) VAT/CST- on sale of goods; (iii) Entry tax- on ...
Read more
GST is levied on every taxable person. Taxable person means a person who carries on any business at any place in India. Such . ..
Read more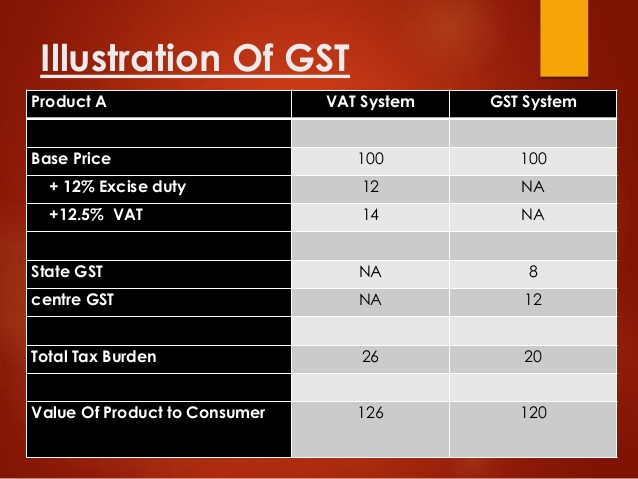
GST is a unified tax which is levied on: (i) goods; (ii) services and (iii) a mix of goods and/or services. Any supply of goods or services . .. ...
Read moreGST India Solution is an effort of firm of professionals who welcome implementation of GST. This is an interactiveplatformthat aspires to disseminate right knowledge to professionals, practitioners and public at large. This platform has beenfloatedbya firm of Chartered Accountants relentlessly working in field of direct and indirect taxes since early 1985.
READ MORE
Our core competence is statutory compliance, advisory, corporate tax planning and appellate matters of direct and indirect taxesandcorporate training sessions on GST.
The senior partner of the firm has to his credit several professional publications viz., Delhi Sales Tax Right to Use Goods Act, Delhi VAT, Maharashtra VAT, West Bengal VAT, Haryana VAT published by Taxmann. Madhya Pradesh VAT and Chhattisgarh VAT were published by Suvidha Law House, Bhopal. He has also addressed seminars on indirect taxes organized by professional bodies like ICAI, IMA, NIFM etc. and has also contributed articles on subjects of pro. . . . .